Introduction to Document Control Vs Document Management
Document Control and Document Management are two processes commonly used to manage documents, data, and information.
There are some significant similarities; they also serve different and distinct purposes and involve different activities.
While they share similarities, they serve different purposes and involve different activities.
Document Control primarily focuses on the accuracy, integrity, and availability of critical documents. In contrast, Document Management encompasses a broader range of activities related to document creation, storage, organization, retrieval, and disposal.
Some critical and significant differences between Document Control and Document Management [Document Control Vs Document Management] are listed below.
What is Document Control System
The Document Control System is a set of processes designed and developed to facilitate and streamline the management of documents within an organization.
It also provides a centralized and structured approach to create, control, track, and distribute documents throughout their lifecycle.
A Document Control System typically includes the following features:
- Document Creation.
- Document Versioning and Revision Control.
- Document Approval Workflow.
- Document Storage and Organization.
- Document Retrieval and Search.
- Document Distribution and Access Control.
- Document Audit Trail and Tracking.
- Document Archiving and Retention.
- Security and Permissions.
Different Types of Control Documents?
Different control documents can exist within an organization to manage and regulate various processes and activities.
Here are some examples:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
- Work Instructions.
- Change Control Documents.
- Quality Control Documents.
- Compliance Documents.
- Audit Documents.
- Specifications and Technical Documents.
- Records and Logbooks.
- Audit Documents
These are just a few examples of control documents, and the specific types used may vary depending on the industry, organizational requirements, and regulatory context.
Control documents play a vital role in ensuring consistency, compliance, and the effective management of processes within an organization.
What is Document Control in QMS?
Documents Control refers to the process and practices in managing and handling documents and controlling documents that are vital for maintaining and demonstrating compliance with quality standards and regulatory requirements.
There are some aspects of Document Control in QMS.
- Document Identification and Classification.
- Document Creation and Approval.
- Document Distribution and Accessibility.
- Version Control and Revision Management.
- Document Retrieval and Obsolescence.
- Change Control and Document Review.
- Document Training and Awareness.
An effective QMS can ensure that proper documents are available to the right people at the precise time in the right format.
Document Control Process with a QMS can provide great consistency, accuracy, and quality standards.
It helps maintain control over critical documents, facilitates efficient document retrieval, supports effective change management, and contributes to the overall effectiveness of the organization’s quality management efforts.
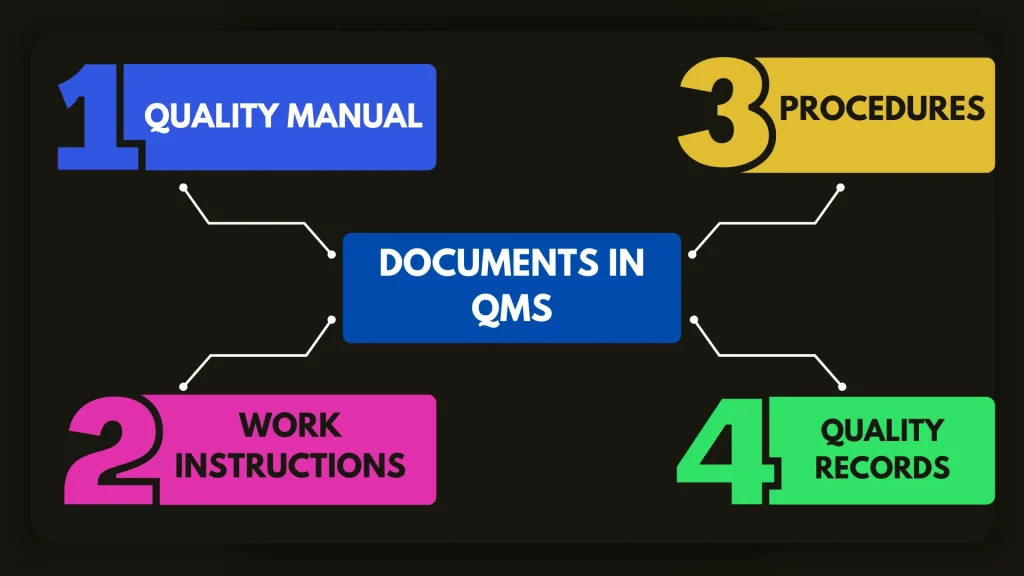
What are the 4 Levels of Documents in QMS?
- Quality Manual.
- Procedures.
- Work Instructions.
- Quality Records.
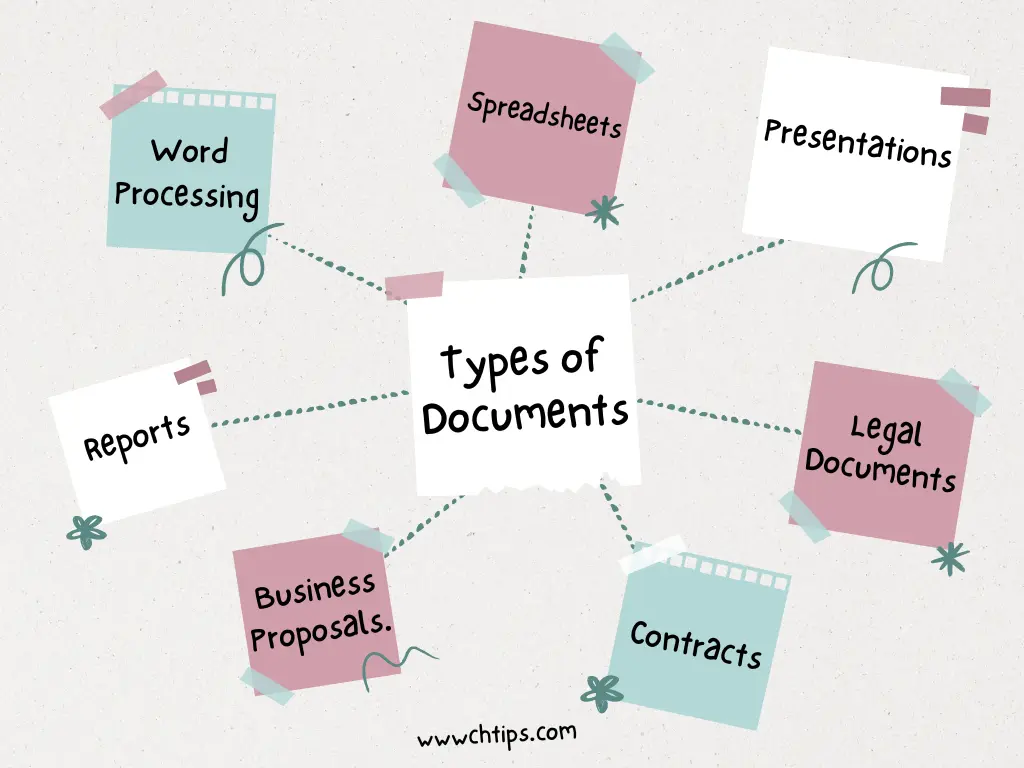
7 Types of Documents?
Different types of documents serve different purposes. Here are 7 types of documents.
- Word Processing Documents.
- Spreadsheets.
- Presentations.
- Reports.
- Business Proposals.
- Contracts.
- Legal Documents.
1. Word Processing Documents.
Word-processing documents are created and maintained using processing software like Microsoft and Google Docs.
These documents are typically used for writing letters, reports, memos, and other textual content.
2. Spreadsheets.
Spreadsheets and created and maintained using programs and software like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets. These spreadsheets are used for organizing, analyzing, and manipulating numerical data.
Spreadsheets provide formulas, functions, and charts to perform calculations and visualize data.
3. Presentations.
The Presentation documents are created using software and programs like Microsoft PowerPoint and Google Slides.
These presentations are information that is presented and delivered visually for better engagement.
They include slides that contain text, images, graphs, and multimedia elements.
4. Reports.
Reports are comprehensive documents that provide detailed information, analysis, and findings on a specific topic or issue.
They are often used in academic, scientific, and business contexts.
Reports typically include an executive summary, introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and recommendations.
5. Business Proposals.
Business proposals outline a project, product, or service to potential clients or investors.
They provide details about the project scope, objectives, timeline, budget, and expected outcomes.
Business proposals aim to convince recipients to accept or invest in the proposed idea or solution.
6. Contracts.
Contracts are legally binding documents establishing rights, obligations, and agreement terms between parties.
They are used in various legal, business, and personal contexts.
Contracts outline the responsibilities, payment terms, deliverables, and dispute resolution mechanisms between the parties involved.
7. Legal Documents.
Legal documents encompass many documents used in legal proceedings, agreements, or transactions.
Examples include wills, deeds, leases, affidavits, court pleadings, contracts, and legal agreements.
Legal documents adhere to specific legal requirements, formats, and terminology.
Example of a Document Management System?
Below I have mentioned some important examples of a Document System.
- Document Storage.
- Version Control.
- Document Collaboration.
- Document Workflow.
- Search and Retrieval.
- Security and Permissions.
- Integration and Extensibility.
What are 5 Examples of File Management?
There are five examples of file management, which are listed below.
- Folder Organization.
- File Naming Conventions.
- Version Control.
- Backup and Recovery.
- Metadata and Tagging.
1. Folder Organization.
File Management allows the creation of a logical folder structure that can be used further for better performance and functions.
The folders are organized into intelligent and meaningful categories and subcategories based on and related to types, sizes, and functions.
For Example, music, documents, images, movies, songs, spreadsheets, and presentations are stored in relevant folders.
2. File Naming Conventions.
File naming conventions use and implement standardized file naming conventions to improve and maintain consistency.
Proper and accurate naming conventions can make searching, acknowledging, and identifying easy.
3. Version Control.
Implementing version control ensures that different iterations or versions of a file are properly managed and tracked.
It involves systematically naming files, using version control software, or utilizing application features to keep track of changes, revisions, and updates.
This helps prevent confusion and allows for easy retrieval of specific versions.
4. Backup and Recovery.
Regularly backing up important files is crucial to protect against data loss due to hardware device failures, accidental deletions, or malware attacks.
Establishing a backup strategy involves creating redundant copies of files on separate storage media or utilizing cloud storage solutions.
5. Metadata and Tagging.
Applying metadata and tags to files provides additional information about the content, making it easier to search and classify documents.
Metadata can include attributes such as author, creation date, keywords, or project details.
Tagging allows for flexible categorization and cross-referencing of files based on specific keywords or attributes, enabling efficient retrieval and organization of files.
These practices contribute to effective file management, promoting organization, accessibility, and productivity while reducing the risk of data loss or confusion.
Document Control Vs Document Management in Tabular Form
Document Control and Document Management are two common but distinct concepts in information management.
There are several significant Differences Between Document Control and Document Management.
Some of them are included below.
| # | Document Control | Document Management |
| 1 | Document Control is the system process regulating an organization’s creation, approval, distribution, and retrieval of documents. It also emphasizes the documents’ nature, such as their accuracy and up to date. | Document Management System is involved in creating, organizing, storing, retrieving, and disposing of documents. It also emphasizes the complete lifecycle of documents starting from creation to destruction. |
| 2 | Document Control primarily controls the management of documents such as organizational processes, quality management systems, compliance requirements, and regulatory standards. | Document Management is widely used for documents, including both formal and informal ones, such as emails, reports, presentations, contracts, and any other files generated within an organization. |
| 3 | Document Control pays attention to the integrity and accuracy of controlled documents. | Document Management works on efficiently organizing, storing, and retrieving documents. |
| 4 | Document Control is particularly important for organizations that must comply with industry-specific regulations, quality standards (e.g., ISO 9001), and legal requirements. | Document Management can also contribute to compliance efforts by providing a centralized document repository. |
| 5 | Works on document approval workflows, version control, document review cycles, change management procedures, and access controls. | Works on document capture and scanning, document storage, metadata management, document retrieval, collaboration tools, and document lifecycle management. |
| 6 | The primary objective of Document Control is to establish and maintain control over important documents, ensuring that they are accurate, up-to-date, and accessible to authorized personnel. | The main objective of Document Management is to facilitate efficient document handling and information flow within an organization. |
| 7 | Document Control often involves implementing workflows and approval processes to ensure documents undergo proper review and authorization before release. | Document Management systems usually offer collaborative features that enable teams to work together on documents, track changes, and manage concurrent editing. |
| 8 | Document Control processes are often designed to handle critical documents and controlled information, emphasizing accuracy and compliance. | Document Management systems are designed to handle large volumes of documents across an organization. |
| 9 | Document Control systems may integrate easily with other quality management systems. | Document Management systems can integrate with various enterprise software, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems. |
| 10 | Document Control places significant emphasis on access control and security measures to prevent unauthorized access, modifications, or distribution of sensitive documents. | Document Management systems provide various levels of access control and security features. |
Document Control primarily concentrates on controlled documents, compliance, and accuracy.
While Document Management encompasses a broader range of documents and emphasizes efficiency, collaboration, and access to information.
Both disciplines play vital roles in effective information management and can be complemented by implementing appropriate processes and technologies tailored to an organization’s needs.
Useful Video: Document Control Vs Document Management
Recommended Reading
- Knowledge Management vs Document Management
- Differences Between Typewriter and Computer keyboard
- Machine Learning Vs Computer Vision
- Difference Between Ecommerce and Woocommerce
- Differences Between General Purpose Computers and Special Purpose Computers
- 5 Differences Between BIOS Bin and BIOS Exe
- 10+ Differences Between Fixed And Removable Disk Drives
- Differences Between Thermal Printers and Dot Matrix Printers
- Differences Between Personal Computers and Mobile Devices
- 11+ Differences Between Optical Disk and Hard Disk
- 8+ Differences Between Multi-Programming OS and Time Sharing OS
- Differences Between HTML and WML- HTML VS WML
- Differences Between Binary Code Decimal and Binary Number System
- 11+ Differences Between OCR and ICR [OCR Vs ICR]
- 15+ Advantages & Benefits of Document Management System
- Smart Search Document Management System
- Differences Between
- Computer Basic Tutorials
Document Control Vs Document Management PDF Download
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQs] on Document Control Vs Document Management
What are the 4 kinds of documents?
Learning-oriented tutorials.
Goal-oriented how-to guides.
Understanding-oriented discussions.
Information-oriented reference material.
Two main types of documents?
Digital and Non-Digital.
What are the 2 Types of File Management?
Types of file management in operating systems are relational, network, and hierarchical.
What are the 6 Types of Files?
JPEG.
PNG.
GIF.
PDF.
SVG.
MP4.
3 Components of File Management?
Data storage, file metadata, and the filesystem.
What are the four main file types?
Document, image, video, and audio.
Three functions of a document management system?
Capture, store and distribute documents.
Get In Touch
I have also written and compiled some articles on computers and telecommunications, and please go through them.
I hope you will like reading it.
All the questions and queries related to the Differences Between document control and document management, with examples and images, have been answered here.
If you have any questions related to document control vs document management.
Don’t hesitate to contact me, and if you need to add, remove or update anything from the article, please let me know in the comment section or via email.
I will be more than happy to update the article. I am always ready to correct myself.
Please share this article with your friends and colleagues; this motivates me to write more on related topics.
!!! Thank You !!
