In today’s post, we are going to learn what is cache memory in a computer. and advantages and disadvantages of cache memory in computer systems with benefits and drawbacks.
The cache memory is a very high-speed semiconductor computer memory used to enhance the speed of the central processing unit {CPU}.
The cache memory is primarily used to store and handle programs and applications which are more frequently used by processors.
The cache memory is also responsible for the high performance of the CPU of the computer system, as the response time for data exchange, access, and transfer is quite low.
The cache memory is also called “Temporary Memory”.
Due to some of the silent features of cache memory, it is used globally to enhance the performance of the processor .
There are still some pros and cons of cache memory, which we are going to discuss briefly in this article.
What is Cache Memory?
Cache memory is a very high-speed memory and is installed near the processor.
It is a type of volatile memory that also provides high-speed data access and exchange to the processor.
They also are helpful in storing computer programs, applications, and data with information.
Whenever any processing data is requested which has already had a sample in the cache memory, then it does not need to go to the main memory or to the hard disk to fetch the data.
The cache memory is the fastest memory available and it acts as a buffer between RAM and the CPU (Central Processing Unit).

The processor checks even if a corresponding entry is available in the cache every time it needs to read or write a location.
Hence, it reduces the time which is required to access the information from the main memory.
Hardware Cache is also called a processor cache and a physical component of the processor, it depends on how close the cache is to the processor core.
It can be a primary and secondary cache memory.
The primary memory cache is directly joined to the processor. The speed depends on the closeness and size of the cache.
The more data is stored in the cache, the fast is processing and the small storage capacity of the chip results in slower processing.
The data present in the cache memory results in fast processing, and vice versa the data present in the cache has fewer data and information, which results in slow speed and data exchange.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cache Memory With Infographic

Advantages of Cache Memory
- The cache is a faster and smaller memory used for storing the data and is used more frequently from the main memory locations.
- A mapping function is used to correspond to the main memory block in the cache memory.
- A primary cache has a less access time comparable to a processor register and it is always placed on the processor chip.
- The secondary cache is mentioned as the level 2 cache and it is also placed in the processor chip.
- It is generally placed between the primary cache and the rest of the memory.
- Cache memory is faster than main memory as a result of two main reasons they are.
- Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) is used in cache memory, on the other hand, main memory uses Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM).
- Cache memory stores the instructions which may be required by the processor next time; as it helps in recovering the information faster as compared to Random Access Memory (RAM).
- It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stored programs that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores data, instructions & information for a limited period.
- Cache memory is high-speed semiconductor memory that can speed up the CPU.
- It makes the computer system more speedy.
Disadvantages of Cache Memory
- This memory is more expensive than other memory like primary memory and secondary memory.
- The storage capacity is completely in use.
- Cache stores the data temporarily.
- If the computer is turned off, the data stored in them is not saved it gets destroyed.
- Cache memory comes at an increased marginal cost than main memory which can increase the cost of the overall system.
- The increased chip area is required for the memory system.
- Cache data is stored as long as the computer power is on.
- It is a volatile memory.
You May Also Like
- What is Cabinet in Computer
- What is Volatile Storage Devices
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Satellite Communications
- Advantages and Disadvantages of USB Flash Drives
- 12 Examples of Secondary Memory in Computer Systems
- 13+ Characteristics of Primary Memory
- What is Buffered Memory and Their Differences
- Characteristics of Virtual Memory in Computer
- Learn Computer Fundamentals
- Computer Basic Tutorials
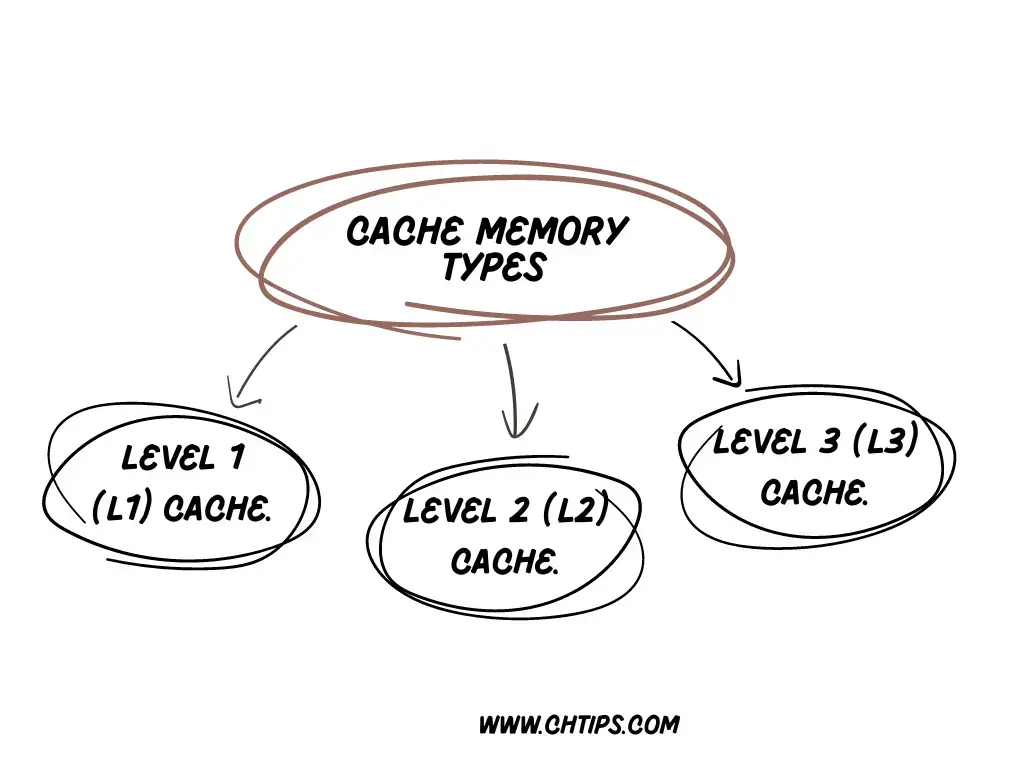
Types of Cache Memory
There are three types of Cache memory they are:
- Level 1 (L1) Cache.
- Level 2 (L2) Cache.
- Level 3 (L3) Cache.
1. Level 1 (L1) Cache or Primary Cache
It is the primary type of cache memory.
The size of the L1 cache is very small as compared to the other cache and the size is between 2 KB to 64 KB size of the cache is depending upon the computer processor.
It is an embedded register in the microprocessor (CPU).
L1 cache first searches which are the instructions required by the CPU.
Examples of registers are an accumulator, an address register, and Program counter, etc.
2. Level 2 (L2) Cache or Secondary Cache
It is the Secondary type of memory.
The size of the L2 cache is more than the L1 which is between 256 KB to 512 KB and it is located on the computer microprocessor.
If the searching instruction was not found in the L1 cache then searching was continued in the L2 cache by a computer microprocessor.
3. Level 3 (L3) Cache or Main Memory
The L3 cache is larger in size and slower in speed as compared to L1 and L2 and its size is between 1MB and 8MB.
In Multicore processors each core they have a separate L1 and L2 but between all these all cores share a common L3 cache.
L3 cache is double in speed compared to RAM.
Useful Video : Cache Memory
Examples of Cache Memory
Cache memory is the fastest volatile computer memory that holds and stores frequently used data and information for more immediate access time taken by the central processing unit.
There are various examples of cache memory that are included.
- Processor Cache.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
- DNS Caches.
- Web Browsers.
- Hard Drive and Solid-State Drive (SSD).
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs).
As mentioned earlier, the cache memory is used and utilized for different purposes.
This cache memory can help in faster data access, considerably reducing the operation time.
Importance of Cache Memory
Cache memory extensively helps in improving and enhancing the overall system performance.
There are a few importance of cache memory that are mentioned below.
- Faster Data and Information Access.
- Reduced Memory Latency.
- Enhance System Performance.
- Bandwidth Conservation.
- Cost-Effective Performance.
- Real-time Applications.
- Improved CPU Utilization.
Functions of Cache Memory
The cache memory can access the data faster than the primary and secondary memory.
Whenever the computer needs to access data, the cache memory comes into play.
It provides the processor with the most frequently requested data.
Cache memory increases performance and allows faster retrieval of data.
The most recent processed data is stored in the cache memory. The CPU can access the data more quickly compared to data in RAM.
Whenever the microprocessor starts processing the data, it first checks in cache memory.
The size of each cache block ranges from 1 to 16 bytes.
Every location has an index that corresponds to the location which has data to access this index is known as address.
Characteristics of Cache Memory
- Cache memory is a very high-speed semiconductor memory.
- These are known as semiconductor memories.
- Data is lost in case the power is lost or the system is switched off.
- It is used to hold those parts of data and programs which are most frequently used by the CPU.
- Cache memory is faster than the main memory or primary memory.
- It consumes less time to access anything as compared to the main memory.
- It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores the data for temporary use.
Types of Primary Memory
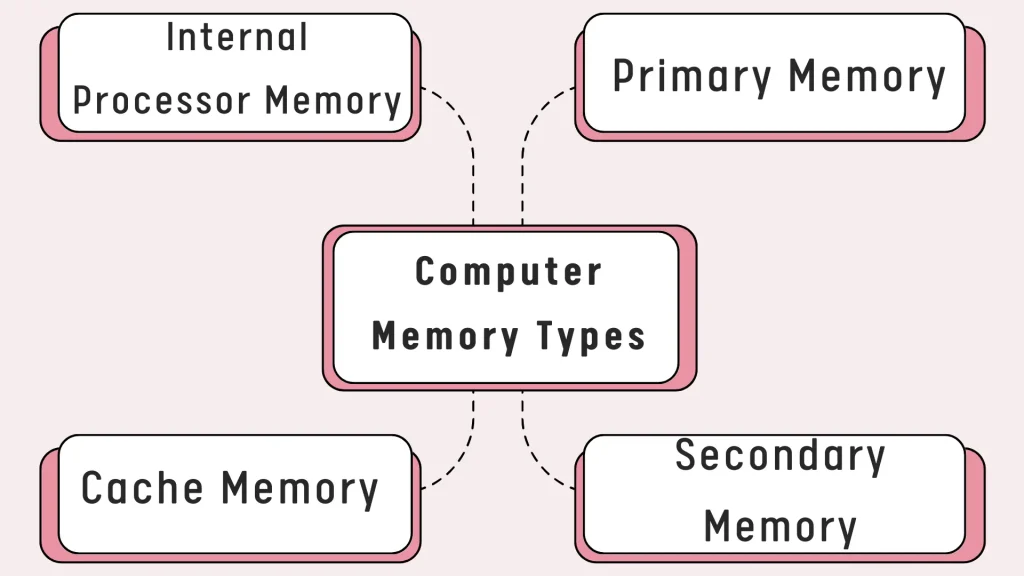
- Internal Processor Memory
- Main memory | RAM (Random Access Memory) | Primary Memory
- Cache Memory
- Storage | Secondary Memory
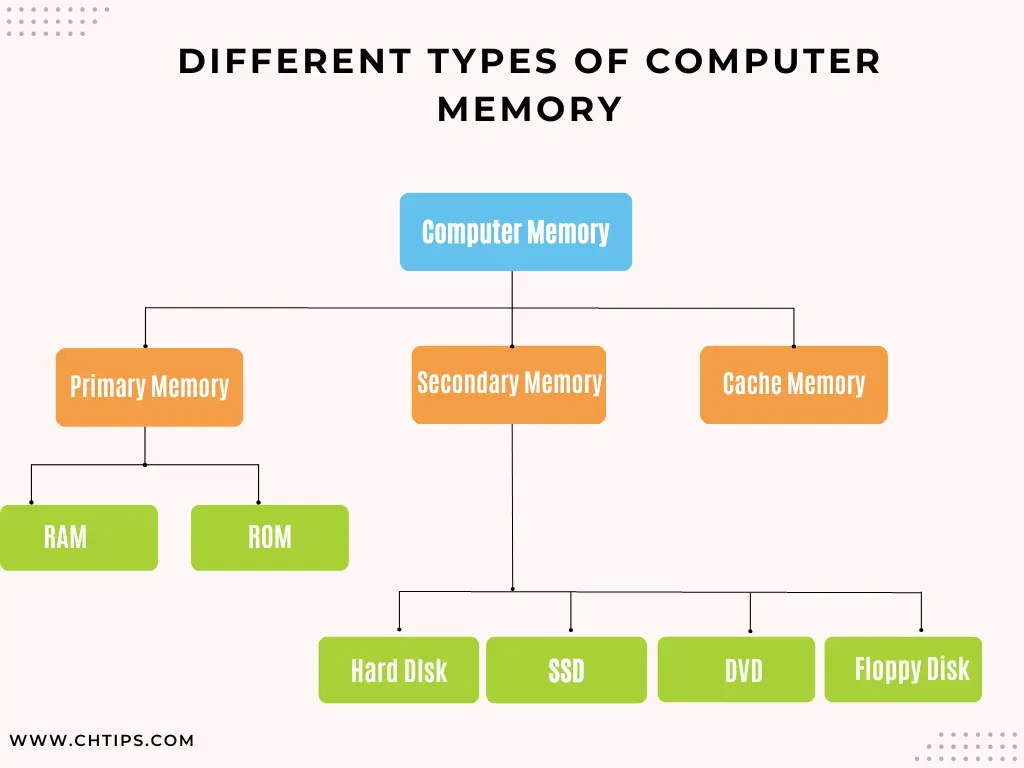
Types of Secondary Memory
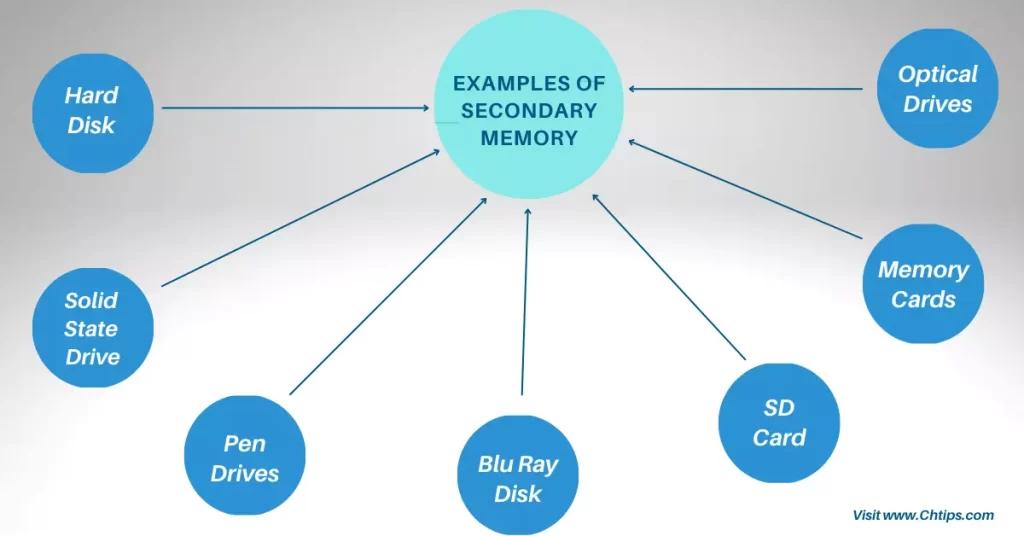
- Hard Disk
- Solid-State Drive
- Pen Drive
- Blu Ray Disk
- SD Card
- CD Drive
- DVD Drive
- Memory Cards
- Floppy Disks
- Disk Packs
- Paper Storage (Punched Tapes, Punched Cards)
- Magnetic Tapes
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQs]
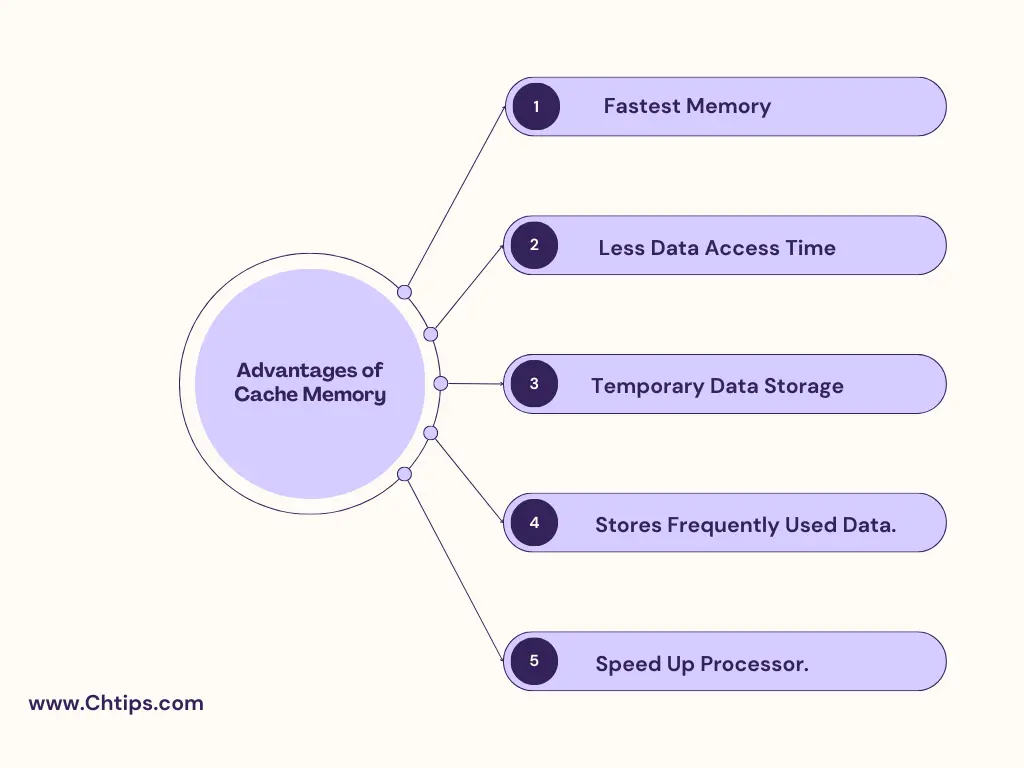
5 Benefits of Cache Memory
1. Cache Memory is the fastest compared to other memory.
2. Less data access time.
3. Temporary data storage.
4. Stores frequently used data and information.
5. Speed Up Processor.
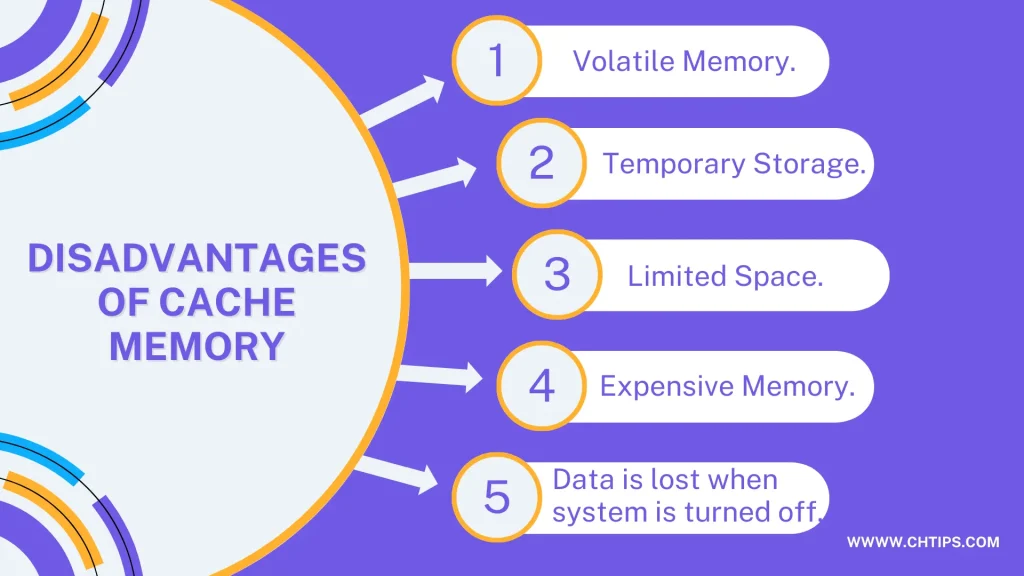
5 Drawbacks of Cache Memory
1. Volatile Memory.
2. Temporary Storage.
3. Limited Space.
4. Expensive Memory.
5. Data is lost when system is turned off.
Is cache memory volatile?
Yes, it tends to lose data when power is off.
What is cache memory example?
CPU Cache.
Which cache memory is better?
L1 Cache.
What is cache for CPU?
Cache for CPU is called “CPU cache memory”.
Get in Touch
I have also written and compiled some articles on computers and telecommunications, and please go through them.
I hope you will like reading it.
I hope that all the questions and queries related to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Cache Memory with Benefits and Drawbacks of Cache Memory have been answered here.
If you have any questions related to the Pros and Cons of Cache Memory in Computer systems and Architect.
Don’t hesitate to contact me, and if you need to add, remove, or update anything from the article, please let me know in the comment section or via email.
I will be more than happy to update the article. I am always ready to correct myself.
I was hoping you could share this article with your friends and colleagues; this motivates me to write more on related topics.
!!! Thank You !!!